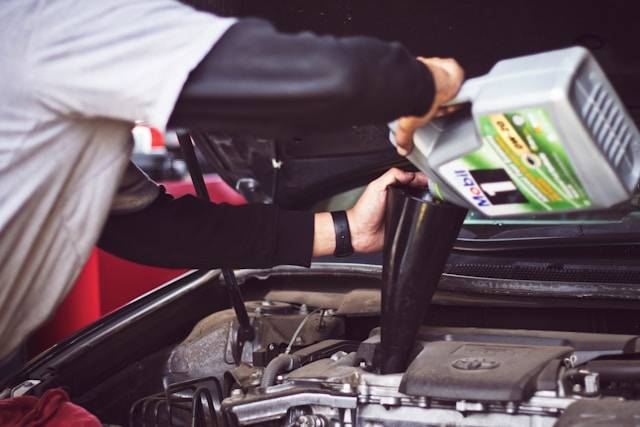
Lubricating an engine effectively is crucial for ensuring its longevity and optimal performance. Here are several ways to lubricate an engine:
1. Engine Oil
Types:
Conventional Oil: Derived from crude oil and suitable for regular driving conditions.
Synthetic Oil: Engineered with chemical additives to provide superior performance, especially in extreme conditions.
Synthetic Blend: A mix of synthetic and conventional oils, offering a balance of performance and cost.
High-Mileage Oil: Formulated with additives to help reduce oil consumption, leaks, and oil seepage in older engines.
Function:
– Reduces friction between moving parts.
– Cools the engine by dissipating heat.
– Cleans by carrying away contaminants.
– Protects against rust and corrosion.
2. Oil Additives
Additives can enhance the properties of engine oil, offering additional protection and performance benefits:
– **Detergents:** Keep engine parts clean by preventing deposit formation.
– **Dispersants:** Prevent sludge and varnish from forming.
– **Antioxidants:** Prevent oxidation and oil thickening.
– **Anti-Wear Agents:** Provide a protective layer on engine parts to minimize wear.
– **Friction Modifiers:** Reduce friction to improve fuel efficiency.
### 3. **Grease**
Used in specific engine components that require thicker lubrication, such as:
– **Wheel Bearings**
– **U-joints**
– **Suspension Components**
### 4. **Graphite or Molybdenum Disulfide Lubricants**
These are used in high-temperature applications where conventional oils may not perform well. They are especially useful in:
– **Piston rings**
– **Cylinder walls**
### 5. **Dry Lubricants**
Such as PTFE (Teflon) and silicon-based lubricants, used in specific applications where oil might attract too much dirt or where liquid lubricants can’t be used.
### 6. **Engine Flush**
Periodically, an engine flush can be used to clean out sludge and deposits from the lubrication system. This process involves adding a chemical flush to the old oil, running the engine for a short period, and then draining it along with the old oil.
### 7. **Proper Maintenance**
– **Regular Oil Changes:** Following the manufacturer’s recommended oil change intervals ensures the engine is always protected by fresh, clean oil.
– **Oil Filter Replacement:** Replacing the oil filter with each oil change ensures contaminants are effectively removed from the oil.
– **Monitoring Oil Levels:** Regularly checking and maintaining the correct oil level helps prevent engine damage.
### 8. **Break-in Oil**
For new or rebuilt engines, break-in oil with high zinc content helps in properly seating the engine components and providing initial lubrication.
### Conclusion
Each lubrication method and product type serves a specific purpose and application within an engine. Properly selecting and maintaining the right lubricants is essential for engine health, performance, and longevity. Regular maintenance and adherence to manufacturer recommendations are key to ensuring your engine remains well-lubricated and runs smoothly.